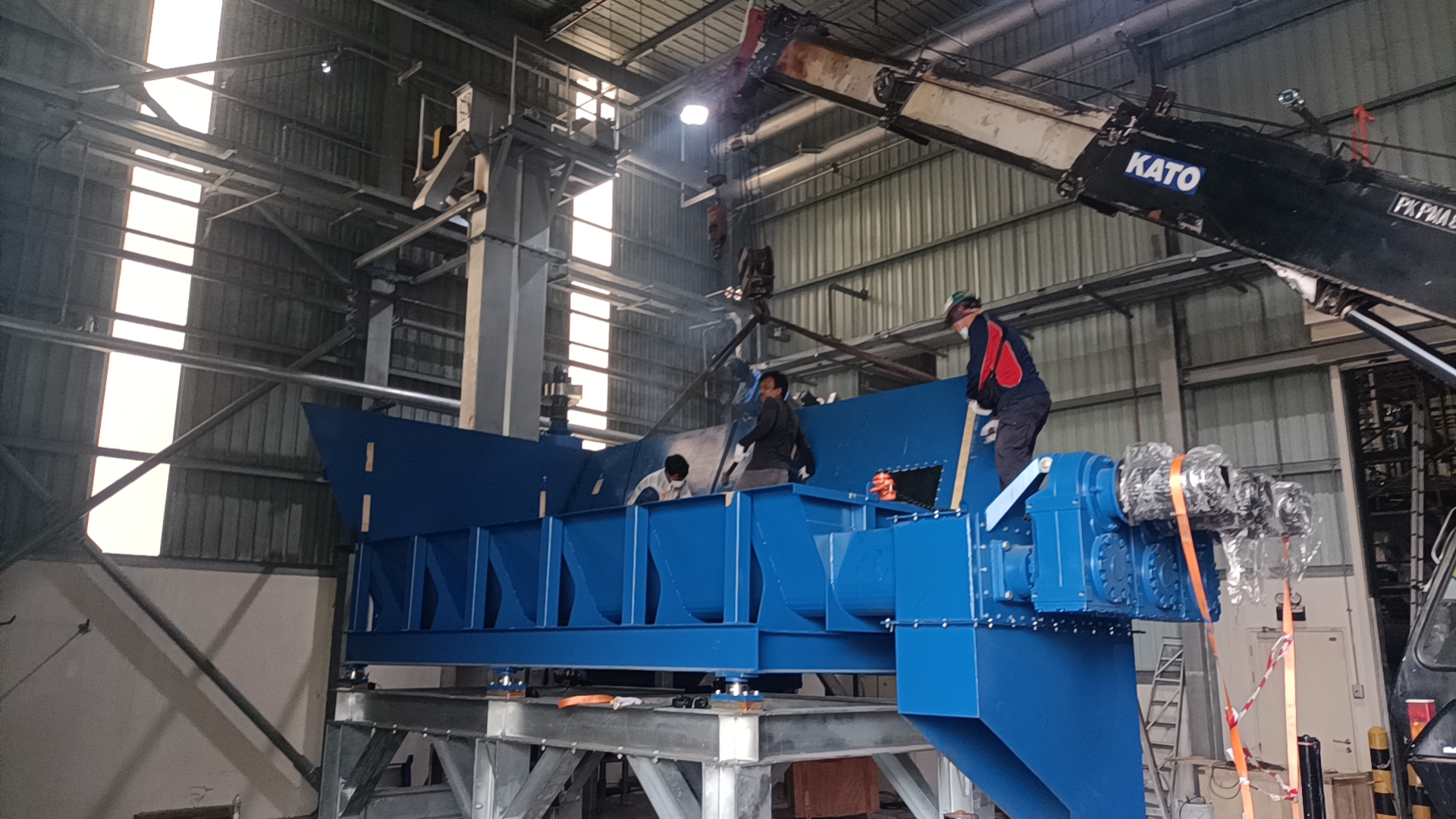
Conveyor Screw: A Comprehensive Guide to Design and Functionality
Conveyor Screw: A Comprehensive Guide to Design and Functionality
Conveyor screw are an essential component of many industrial processes. They are used to move materials from one place to another, such as from a hopper to a processing machine or from one part of a production line to another. Conveyor screws are also known as augers, and they come in a variety of sizes and shapes to suit different applications.
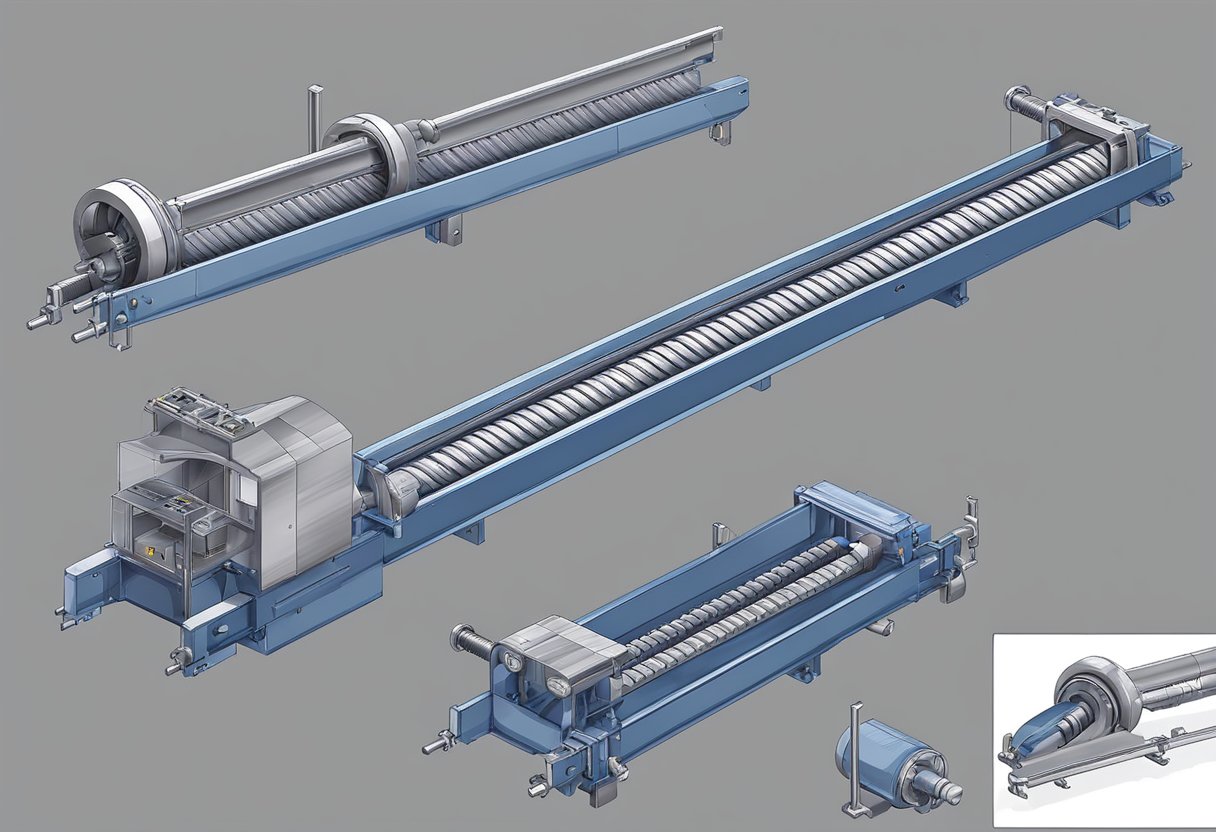
The design of a conveyor screw is critical to its effectiveness. The screw must be able to move the material smoothly and efficiently, without causing damage or blockages. The size and shape of the screw, as well as the speed at which it rotates, must be carefully chosen to suit the material being moved and the specific requirements of the process. In addition, the material of the screw must be chosen carefully to ensure that it is strong enough to withstand the stresses of the process.
History of Conveyor Screws

Conveyor screws, also known as auger conveyors, have been in use for thousands of years. The ancient Greeks and Romans used similar devices to transport water for irrigation and mining.
In the 19th century, screw conveyors were used in the agricultural industry to move grain and other crops. They were also used in mining and construction to move bulk materials such as coal and gravel.
The first patent for a screw conveyor was filed in 1898 by William E. Sproule, who designed a screw conveyor to move coal and other materials for the Pennsylvania Coal Company. Since then, conveyor screws have been used in a variety of industries, including food processing, chemical manufacturing, and wastewater treatment.
Today, conveyor screws come in a variety of sizes and configurations to meet the needs of different industries. They can be made from a variety of materials, including stainless steel, carbon steel, and plastic. Conveyor screws are an efficient and cost-effective way to move bulk materials, and they continue to be an important part of many industrial processes.
Design and Mechanics

Helix Geometry
The helix geometry of a conveyor screw is a critical factor in its design and performance. The pitch of the helix determines the amount of material moved per revolution, while the diameter of the screw affects the speed and torque required to move the material. The helix angle also plays a role in the efficiency of the conveyor, as a steeper angle can increase the rate of material flow but may require more power to operate.
Shaft Configurations
The shaft configuration of a conveyor screw is another important aspect of its design. A solid shaft provides greater strength and rigidity, while a hollow shaft can reduce weight and allow for cooling or heating of the material being conveyed. Flights can be welded directly to the shaft or mounted on a separate hub, and the shaft can be supported by bearings at one or both ends.
Material Considerations
The choice of material for a conveyor screw depends on a variety of factors, including the properties of the material being conveyed, the environment in which the conveyor will operate, and the desired service life of the screw. Common materials include carbon steel, stainless steel, and various alloys, each with their own strengths and weaknesses. Coatings or surface treatments may also be applied to improve wear resistance or prevent corrosion.
In summary, the design and mechanics of a conveyor screw are essential to its performance and longevity. The helix geometry, shaft configuration, and material selection must be carefully considered to ensure efficient and reliable operation.
Types of Conveyor Screws
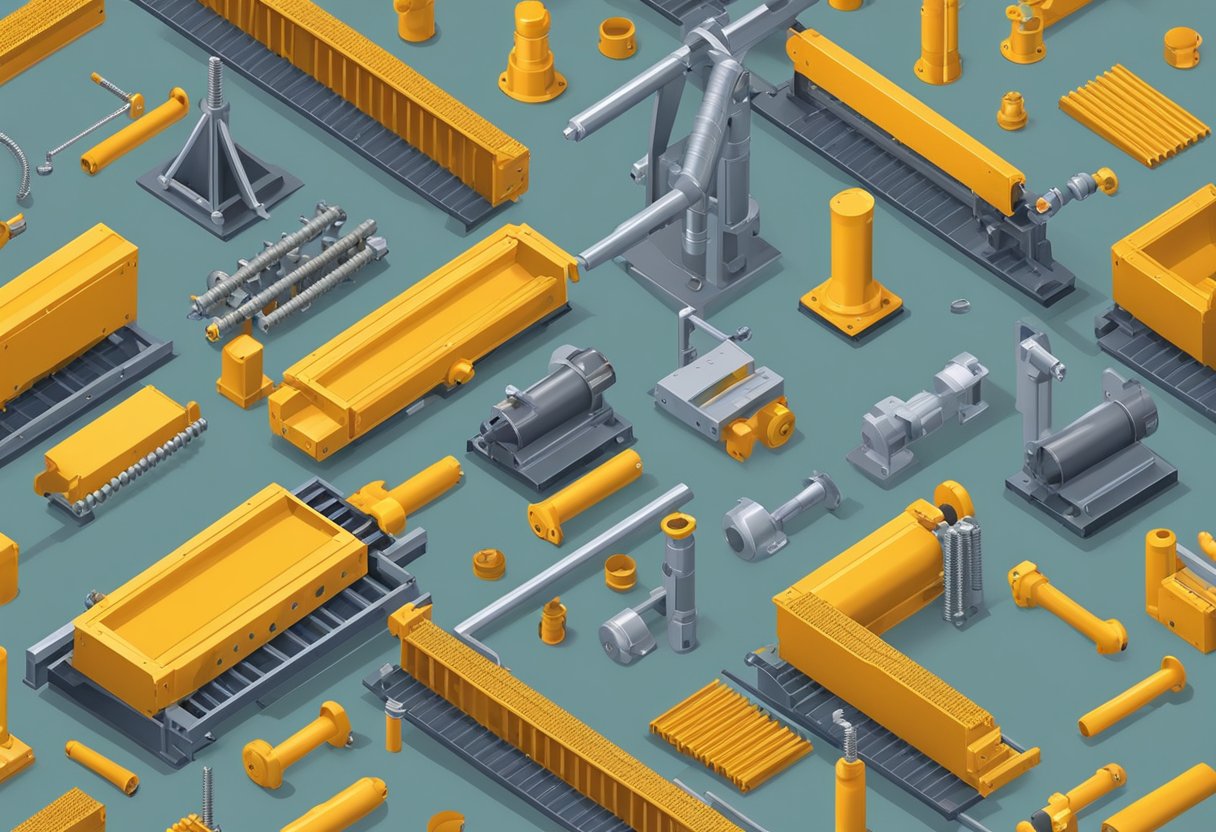
Flexible Screw Conveyors
Flexible screw conveyors, also known as auger conveyors, are designed to move materials through a tube or channel using a rotating helical screw blade. These conveyors are highly versatile and can handle a wide range of materials, including powders, granules, and even larger items like fruits and vegetables. The flexible design of these conveyors allows them to easily navigate around corners and obstacles, making them ideal for use in tight spaces.
Shaftless Screw Conveyors
Shaftless screw conveyors are similar to flexible screw conveyors in that they use a rotating helical screw blade to move materials through a tube or channel. However, unlike flexible screw conveyors, shaftless screw conveyors do not have a central shaft, which makes them ideal for handling sticky or viscous materials that may clog traditional screw conveyors. They are also easier to clean and maintain than traditional screw conveyors.
Multiple Start Screws
Multiple start screws, also known as double flight screws, are designed to move materials more quickly and efficiently than traditional single flight screws. These screws have multiple threads or flights wrapped around a central shaft, which allows them to move more material with each rotation. Multiple start screws are ideal for use in applications where high capacity and efficiency are required, such as in the food and beverage industry.
In summary, there are several types of conveyor screws available, each with its own unique advantages and applications. By understanding the differences between these types of screws, businesses can choose the conveyor system that best meets their needs and requirements.
Manufacturing Processes
Fabrication Techniques
Conveyor screws are manufactured using various fabrication techniques, including cold rolling, hot rolling, and machining. The choice of technique depends on the material being used, the desired screw diameter and pitch, and the production volume.
Cold rolling is the most common fabrication technique used for conveyor screws. It involves feeding a flat strip of metal through a set of rollers to form a helix. This process is preferred for producing small to medium-sized screws with a diameter of up to 24 inches.
Hot rolling is used for larger screws with a diameter of up to 60 inches. In this process, a heated metal billet is passed through a series of rollers to form a helix. Hot rolling is preferred for producing screws from materials that are difficult to cold roll.
Machining is used for producing screws with a diameter of over 60 inches. This process involves cutting a helix from a solid metal block using a lathe or a milling machine.
Quality Control
Quality control is an important aspect of conveyor screw manufacturing. To ensure that the screws meet the required specifications, various quality control measures are implemented throughout the manufacturing process.
One of the quality control measures is material inspection. The raw materials used for manufacturing conveyor screws are inspected for defects such as cracks, voids, and inclusions. Only high-quality materials that meet the required specifications are used for screw fabrication.
Another quality control measure is dimensional inspection. The screws are inspected for dimensional accuracy using specialized equipment such as coordinate measuring machines (CMMs) and optical comparators. This ensures that the screws meet the required diameter, pitch, and helix angle specifications.
In addition to material and dimensional inspection, other quality control measures such as visual inspection, non-destructive testing, and surface finish inspection are also implemented to ensure that the conveyor screws meet the required quality standards.
Applications and Uses

Agriculture
Conveyor screws are widely used in the agriculture industry for various tasks such as conveying grains, seeds, and other materials. They are used in grain elevators, feed mills, and other agricultural facilities. Conveyor screws can be used for both horizontal and inclined conveying, making them a versatile solution for many agricultural applications.
Food Industry
The food industry is another area where conveyor screws are commonly used. They are used to move food products through different stages of production such as mixing, cooking, and packaging. Conveyor screws are also used for transporting food products between different areas of the production facility. They are easy to clean and maintain, which is essential in the food industry to ensure food safety.
Pharmaceuticals
In the pharmaceutical industry, conveyor screws are used to transport and mix powders, granules, and other materials. They are used in the production of tablets, capsules, and other pharmaceutical products. Conveyor screws are designed to meet strict hygiene and safety standards, making them suitable for use in pharmaceutical production facilities.
Overall, conveyor screws are a versatile and reliable solution for many industries and applications. They can be customized to meet specific requirements and are capable of handling a wide range of materials. With proper maintenance and care, conveyor screws can provide years of efficient and trouble-free operation.
Installation and Maintenance
Installation Guidelines
When installing a conveyor screw, it is important to follow certain guidelines to ensure optimal performance and longevity. The following steps should be taken during installation:
- Ensure that the conveyor screw is properly aligned with the motor and other components.
- Use high-quality fasteners to secure the conveyor screw in place.
- Lubricate all moving parts before operation.
- Check for any loose or damaged components before operation.
Following these guidelines will help to prevent issues such as misalignment, component failure, and premature wear.
Routine Maintenance
Regular maintenance is essential to keep a conveyor screw operating at peak performance. The following maintenance tasks should be performed regularly:
- Check for signs of wear on the conveyor screw and other components.
- Lubricate all moving parts.
- Tighten any loose fasteners.
- Check for proper alignment between the conveyor screw and other components.
- Clean the conveyor screw and surrounding area to prevent buildup of debris.
Performing these tasks on a regular basis will help to prevent premature wear and ensure optimal performance.
Troubleshooting
Despite proper installation and maintenance, issues may still arise with a conveyor screw. The following troubleshooting steps should be taken if issues are encountered:
- Check for any loose or damaged components.
- Ensure that the conveyor screw is properly aligned with other components.
- Check for proper lubrication of all moving parts.
- Inspect the conveyor screw for signs of wear or damage.
- Clean the conveyor screw and surrounding area to prevent buildup of debris.
If issues persist, it may be necessary to consult with a professional for further assistance.
By following these installation and maintenance guidelines, a conveyor screw can provide reliable and efficient performance for many years.
Safety and Compliance

Operational Safety
Conveyor screws are powerful machines that can move heavy materials quickly and efficiently. However, they can also be dangerous if not operated properly. It is important to follow all safety guidelines when working with conveyor screws to prevent accidents and injuries.
One of the most important safety measures is to ensure that all guards and safety devices are in place and functioning properly. Workers should also be trained on how to safely operate and maintain the machine. This includes wearing appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) such as gloves, safety glasses, and hard hats.
Another key safety consideration is to avoid overloading the conveyor screw. Overloading can cause the machine to malfunction and potentially cause damage or injury. It is important to follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for maximum weight capacity and to regularly inspect the machine for signs of wear or damage.
Regulatory Standards
In addition to following operational safety guidelines, it is also important to comply with regulatory standards when working with conveyor screws. These standards are in place to ensure that the machine is safe and reliable for workers to use.
One important regulatory standard is the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) guidelines for machine guarding. These guidelines require that all machinery be guarded to prevent workers from coming into contact with moving parts. Conveyor screws must also comply with other OSHA regulations such as lockout/tagout procedures and electrical safety standards.
Other regulatory standards that may apply to conveyor screws include the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) guidelines for combustible dust and the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) guidelines for safety signs and labels.
By following operational safety guidelines and complying with regulatory standards, workers can help ensure that conveyor screws are used safely and effectively.
Innovations and Developments
Material Advancements
In recent years, conveyor screw manufacturers have made significant advancements in the materials used to construct their products. One of the most notable developments has been the use of composite materials, such as carbon fiber and fiberglass, which offer improved strength and durability over traditional materials like steel and aluminum.
These composite materials are also lighter in weight, which can reduce the overall weight of the conveyor system and improve energy efficiency. Additionally, some manufacturers have begun using materials that are more resistant to corrosion and wear, such as ceramics and polymers, to extend the lifespan of their products and reduce maintenance requirements.
Design Improvements
Along with material advancements, conveyor screw manufacturers have also made significant improvements in the design of their products. One notable development has been the use of 3D modeling software to optimize the shape and size of the screw, resulting in improved performance and efficiency.
Another design improvement has been the use of variable pitch screw designs, which allow for greater control over the flow of materials and can improve the accuracy of the conveyor system. Additionally, some manufacturers have developed screw designs that are more flexible and can adapt to changes in material properties or flow rates.
Overall, these innovations and developments in materials and design have resulted in conveyor screw systems that are more reliable, efficient, and cost-effective than ever before. As technology continues to advance, it is likely that we will see even more improvements and advancements in the years to come.
Market Trends

Demand Dynamics
The demand for conveyor screws is expected to grow steadily in the coming years. The primary factor driving the demand is the increasing automation in various industries, including food and beverage, automotive, and packaging. Conveyor screws are widely used in these industries to transport materials and products from one place to another. Moreover, the growing trend of e-commerce and online shopping is also expected to contribute to the demand for conveyor screws as they are used in warehouses and distribution centers for material handling.
Another factor driving the demand for conveyor screws is their efficiency and cost-effectiveness. Conveyor screws are designed to handle a wide range of materials, including bulk materials, powders, and granules. They are also easy to install and maintain, which makes them a popular choice among manufacturers.
Regional Market Insights
North America and Europe are the largest markets for conveyor screws, owing to the presence of a large number of manufacturing industries. In North America, the United States is the largest market for conveyor screws, followed by Canada and Mexico. In Europe, Germany, France, and the United Kingdom are the major markets for conveyor screws.
Asia Pacific is expected to be the fastest-growing market for conveyor screws, owing to the increasing industrialization and urbanization in the region. China, India, and Japan are the major markets for conveyor screws in Asia Pacific. The Middle East and Africa and Latin America are also expected to witness significant growth in the demand for conveyor screws in the coming years.
In conclusion, the demand for conveyor screws is expected to grow steadily in the coming years, driven by the increasing automation in various industries and their efficiency and cost-effectiveness. North America and Europe are the largest markets for conveyor screws, while Asia Pacific is expected to be the fastest-growing market.
Case Studies

Several industries have implemented conveyor screws in their production lines, resulting in increased efficiency and cost savings. Here are a few case studies:
Case Study 1: Food Processing Plant
A food processing plant installed conveyor screws to transport bulk materials such as grains, sugar, and flour. The plant saw a significant reduction in labor costs as the conveyor screws eliminated the need for manual handling of heavy materials. Additionally, the conveyor screws improved the accuracy of material delivery, reducing waste and improving product quality.
Case Study 2: Chemical Manufacturing Facility
A chemical manufacturing facility implemented conveyor screws to move powdered chemicals through their production line. The conveyor screws increased the speed and accuracy of material delivery, resulting in a 30% reduction in production time. The facility also saw a decrease in material waste and improved safety for workers as the conveyor screws eliminated the need for manual material handling.
Case Study 3: Construction Site
A construction site used conveyor screws to transport concrete from the mixer to the pouring location. The conveyor screws allowed for precise delivery of the concrete, reducing waste and improving the quality of the final product. The construction site also saw a 50% reduction in labor costs as the conveyor screws eliminated the need for manual material handling.
Overall, these case studies demonstrate the benefits of implementing conveyor screws in various industries. By improving efficiency and reducing labor costs, conveyor screws can be a valuable addition to any production line.



