
Fat Pump: A Comprehensive Guide to Building Muscle and Burning Fat
Fat Pump: A Comprehensive Guide to Building Muscle and Burning Fat
Fat pump is a new cosmetic procedure that has gained popularity in recent years. It involves using a person’s own fat to enhance certain areas of their body. The procedure is often used to add volume to the breasts, buttocks, or face.

The process of fat pump involves removing fat from a person’s body using liposuction. The fat is then purified and injected back into the desired area. This procedure is often preferred over other cosmetic procedures because it uses the person’s own tissue, reducing the risk of rejection or allergic reactions.
While fat pump is a relatively safe procedure, it is important to note that it is not suitable for everyone. A person’s overall health and medical history must be taken into consideration before undergoing the procedure. Additionally, the results of the procedure may vary and it is important to have realistic expectations.
Fat Pump Fundamentals

Working Principle
A fat pump is a type of positive displacement vacuum pump that is used to move high viscosity fluids such as fats, oils, and greases. The working principle of a fat pump is based on the displacement of a fixed volume of fluid from the inlet to the outlet of the pump. The pump consists of a rotor and a stator, both of which have a unique geometry that creates a series of sealed cavities. As the rotor rotates, the cavities move from the suction side to the discharge side, pushing the fluid along with them.
Types of Fat Pumps
There are two main types of fat pumps: rotary lobe pumps and progressive cavity pumps. Rotary lobe pumps have two or more lobes that rotate inside a casing, creating a series of sealed chambers that move the fluid from the inlet to the outlet. Progressive cavity pumps, on the other hand, consist of a single helical rotor that rotates inside a double helical stator, creating a series of sealed cavities that move the fluid from the inlet to the outlet.
Both types of fat pumps have their advantages and disadvantages. Rotary lobe pumps are better suited for high flow rate applications, while progressive cavity pumps are better suited for high pressure applications. Additionally, rotary lobe pumps are easier to clean and maintain, while progressive cavity pumps are more sensitive to changes in viscosity and require more frequent maintenance.
In conclusion, understanding the fundamentals of fat pumps is essential for selecting the right pump for a specific application. By choosing the right type of pump and understanding its working principle, users can ensure optimal performance and efficiency.
Design and Components
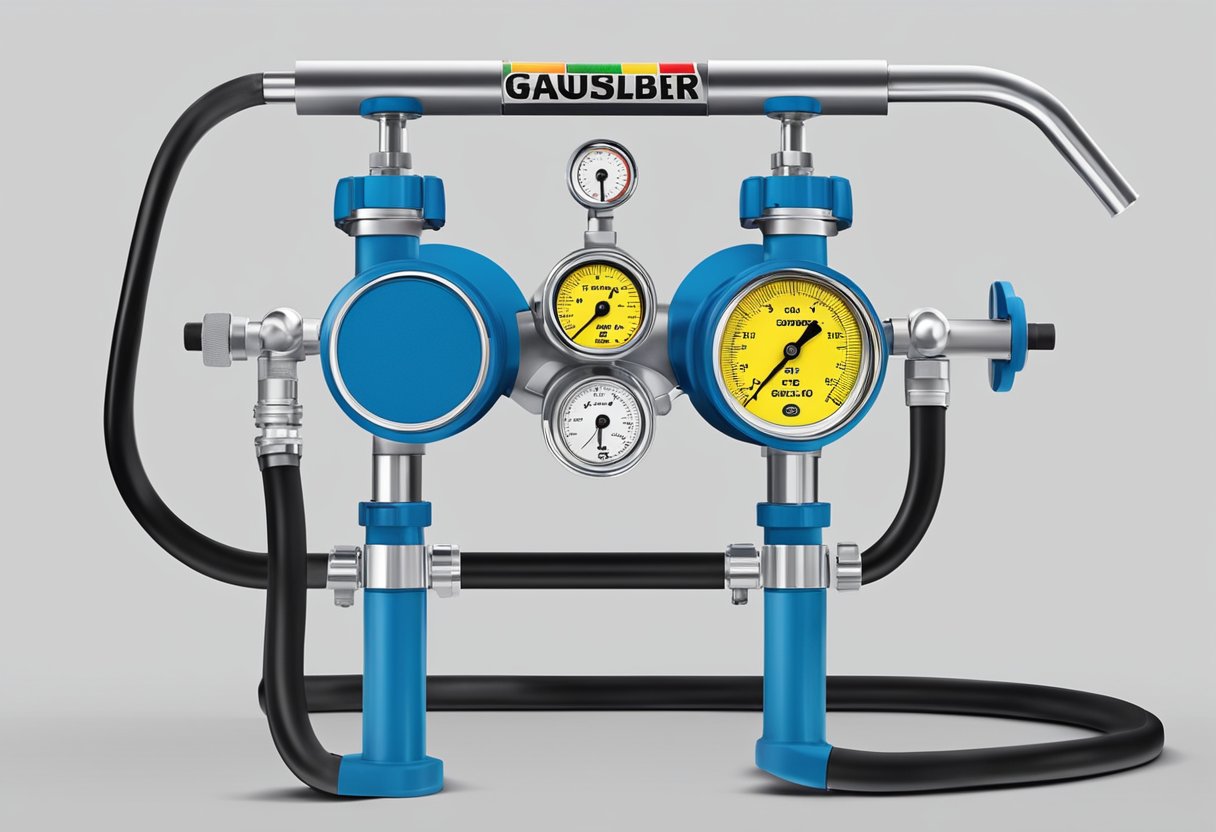
Pump Housing
The Fat Pump is a positive displacement pump that is designed to handle viscous fluids and slurries with high solid content. The pump housing is made of high-quality cast iron, which makes it extremely durable and resistant to wear and tear. It has a unique design that allows it to handle high pressures and flow rates with ease.
The pump housing has an inlet and outlet port, which are both located on the top of the pump. The inlet port is where the fluid enters the pump, while the outlet port is where the fluid exits the pump. The housing is also equipped with a pressure relief valve, which helps to prevent damage to the pump in case of overpressure.
Rotor and Stator
The rotor and stator are the two most important components of the Fat Pump. The rotor is a helical-shaped metal component that rotates inside the stator, which is a rubber-lined tube. The rotor and stator work together to create a series of cavities, which move the fluid from the inlet to the outlet port.
The rotor is designed to fit snugly inside the stator, which creates a tight seal. This seal prevents the fluid from leaking out of the pump and ensures that the pump operates efficiently. The rotor and stator are both made of high-quality materials, which makes them resistant to wear and tear.
In conclusion, the design and components of the Fat Pump make it an ideal choice for handling viscous fluids and slurries with high solid content. Its unique design allows it to handle high pressures and flow rates with ease, while its durable components ensure that it operates efficiently for a long time.
Operational Mechanisms

Displacement Control
Fat pumps operate using a displacement control mechanism. This means that the amount of fat that is pumped is directly proportional to the displacement of the pump. The displacement of the pump is determined by the size of the pump’s internal chambers. As the pump rotates, these chambers fill with fat and then discharge it through the outlet.
The displacement control mechanism is highly accurate and allows for precise control over the amount of fat that is pumped. This is particularly important in applications where precise dosing is required, such as in the food and pharmaceutical industries.
Pressure Regulation
In addition to displacement control, fat pumps also utilize pressure regulation mechanisms. These mechanisms ensure that the pressure of the fat being pumped remains constant throughout the pumping process. This is important because it ensures that the fat is pumped at a consistent rate, which can help to prevent issues such as clogging and blockages.
Pressure regulation mechanisms work by adjusting the speed of the pump based on the pressure of the fat being pumped. If the pressure drops, the pump speeds up to maintain a constant pressure. Conversely, if the pressure increases, the pump slows down to prevent over-pressurization.
Overall, the combination of displacement control and pressure regulation mechanisms makes fat pumps highly accurate and reliable. They are well-suited to a wide range of applications, from food processing to pharmaceutical production.
Application Areas
Food Industry
Fat pumps are widely used in the food industry for various applications such as mixing, transferring, and processing of food products. One of the most common uses of fat pumps in the food industry is for the transfer of liquid and semi-liquid food products such as sauces, soups, and gravies. Fat pumps are also used for the transfer of solid food products such as meat and vegetables.
Fat pumps are also used in the production of dairy products such as cheese, butter, and yogurt. In the production of cheese, fat pumps are used for the transfer of milk and cream. In the production of butter, fat pumps are used for the transfer of cream and for the mixing of the cream to form butter.
Cosmetic Industry
Fat pumps are also used in the cosmetic industry for the production of various cosmetic products such as lotions, creams, and ointments. Fat pumps are used for the transfer of the base ingredients such as oils and waxes, and for the mixing of the ingredients to form the final product.
Fat pumps are also used for the transfer of active ingredients such as vitamins and minerals, and for the mixing of the active ingredients with the base ingredients. Fat pumps are essential in the production of cosmetic products as they ensure that the ingredients are mixed uniformly and that the final product is of high quality.
In conclusion, fat pumps are widely used in the food and cosmetic industries for various applications such as mixing, transferring, and processing of food and cosmetic products. Fat pumps are essential in ensuring that the ingredients are mixed uniformly and that the final products are of high quality.
Installation and Maintenance
Installation Guidelines
Installing a fat pump requires careful consideration of several factors. First, it is important to choose a location that is easily accessible for maintenance and repair. The pump should be installed on a level surface and secured with bolts or anchors to prevent movement during operation.
It is also important to ensure that the pump is properly aligned with the piping system. The alignment should be checked using a laser alignment tool to ensure that the pump shaft is in line with the motor shaft. Any misalignment can cause excessive wear on the bearings and reduce the lifespan of the pump.
The piping system should be designed to minimize friction losses and ensure that the pump operates at its rated flow and pressure. The diameter of the suction and discharge pipes should be selected based on the pump’s flow rate and pressure requirements.
Maintenance Procedures
Regular maintenance is essential to ensure the reliable operation of a fat pump. The following maintenance procedures should be performed at regular intervals:
- Check the oil level in the pump and motor bearings and top up if necessary.
- Inspect the impeller and casing for wear and damage and replace if necessary.
- Check the alignment of the pump and motor shafts and adjust if necessary.
- Inspect the mechanical seal for wear and replace if necessary.
- Check the motor and pump bearings for wear and replace if necessary.
- Clean the strainer and suction pipe to prevent blockages.
It is important to follow the manufacturer’s recommended maintenance schedule to ensure that the pump operates reliably and efficiently. Regular maintenance can also help to prevent costly breakdowns and extend the lifespan of the pump.
Performance Metrics
Efficiency
The efficiency of a fat pump is a critical performance metric that is often measured in terms of the percentage of fat that is extracted from the wastewater. The higher the efficiency, the more fat that is removed, resulting in cleaner wastewater and reduced maintenance costs.
Efficiency is affected by various factors, including the design of the pump, the type of fat being extracted, and the operating conditions. To optimize efficiency, it is important to choose a fat pump that is specifically designed for the type of fat being extracted and to ensure that it is properly installed and maintained.
Flow Rate
Another important performance metric for a fat pump is the flow rate, which is the volume of wastewater that can be processed per unit of time. The flow rate is determined by the size of the pump and the speed at which it operates.
A higher flow rate can increase the efficiency of the fat pump by reducing the amount of time that the wastewater spends in contact with the fat. However, it is important to ensure that the flow rate is not so high that it compromises the efficiency of the fat extraction process.
Overall, the efficiency and flow rate are two critical performance metrics that must be carefully considered when selecting a fat pump. By choosing a pump that is optimized for the specific needs of the application and ensuring that it is properly installed and maintained, it is possible to achieve optimal performance and reduce maintenance costs.
Safety and Compliance
Safety Standards
The Fat Pump is designed to meet the highest safety standards in the industry. The device has undergone rigorous testing to ensure that it is safe for use in medical procedures. The materials used in the device are of the highest quality and are designed to withstand the stresses of medical procedures. The Fat Pump is also designed to be easy to use, with clear instructions and intuitive controls.
Regulatory Compliance
The Fat Pump is compliant with all relevant regulations and standards. The device is classified as a Class II medical device by the FDA, and is CE marked for use in the European Union. The device is also compliant with ISO 13485:2016, the international standard for quality management systems for medical devices.
The Fat Pump is designed to be used by trained medical professionals in a clinical setting. It should only be used for its intended purpose, and all instructions should be followed carefully. The device should be cleaned and maintained according to the instructions provided, and any faults or malfunctions should be reported immediately.
In summary, the Fat Pump is a safe and compliant device that meets the highest standards in the industry. Its safety features and compliance with regulations make it a reliable choice for medical professionals looking to perform fat transfer procedures.
Market Trends
Demand Analysis
The fat pump market has been experiencing steady growth in recent years. This can be attributed to the increasing demand for cosmetic surgeries and the growing awareness about body contouring procedures. According to a report by Allied Market Research, the global fat transfer market is expected to reach $4.1 billion by 2027, growing at a CAGR of 10.1% from 2020 to 2027.
The demand for fat pumps is also increasing due to the rising number of patients opting for autologous fat transfer procedures. These procedures involve transferring fat from one part of the body to another to enhance the appearance of the recipient area. Fat pumps are used to harvest and process fat from the donor area before transferring it to the recipient area.
Technological Advancements
Technological advancements have been a driving force behind the growth of the fat pump market. Manufacturers are constantly innovating to develop more efficient and user-friendly products. For instance, some fat pumps now come with touch screen interfaces that make it easier for surgeons to control the device and monitor the progress of the procedure.
There has also been a shift towards using closed-system fat transfer devices to reduce the risk of infection and contamination. These devices are designed to minimize the exposure of the harvested fat to the external environment, thereby reducing the risk of bacterial contamination.
Overall, the fat pump market is poised for significant growth in the coming years, driven by the increasing demand for cosmetic surgeries and technological advancements in the field.
Categories
Recent Posts
-

What is harmless treatment of sick and dead animals and poultry(rendering plant) A Key Initiative to Protect the Ecological Environment and Food Safety.
March 6, 2025 -

How does Sunrise rendering plant equipment destroy avian influenza viruses in livestock poultry carcasses
March 5, 2025 -

Sunrise Rendering Thailand Exhibition
March 5, 2025
