Screw Conveyors: An Overview of their Function and Applications
Screw Conveyors: An Overview of their Function and Applications
Screw conveyors are a type of mechanical conveying system that are widely used in various industries for transporting bulk materials. These conveyors consist of a rotating screw inside a trough or tube, which moves the material along the length of the conveyor. Screw conveyors are known for their versatility and efficiency, as they can handle a wide range of materials and can be customized to fit specific applications.
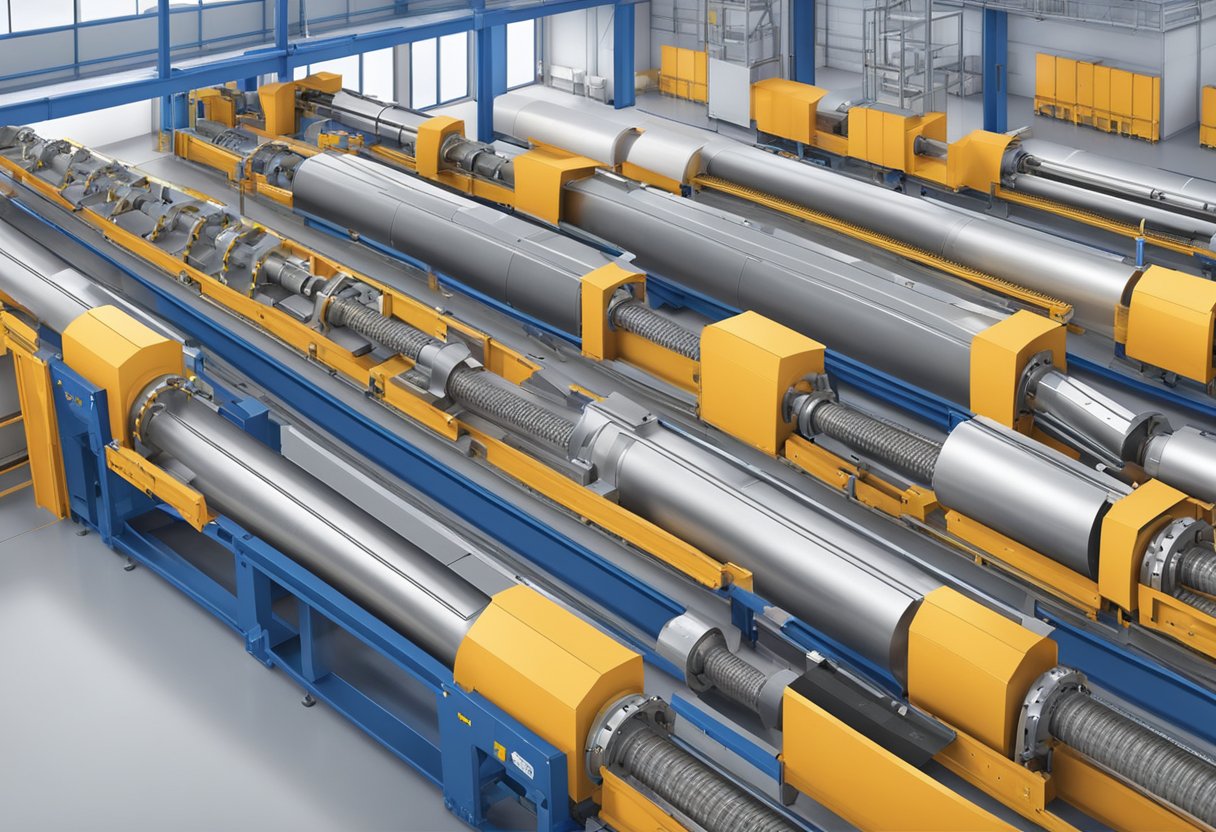
One of the main advantages of screw conveyors is their ability to handle materials that are difficult to transport using other types of conveyors. For example, they can handle materials that are sticky, abrasive, or have a tendency to clump together. Additionally, screw conveyors are relatively simple in design and can be easily customized to fit specific applications, making them a popular choice for many industries.
Despite their advantages, screw conveyors do have some limitations. For example, they may not be suitable for materials that are very fine or have a tendency to pack tightly. Additionally, screw conveyors may not be the best choice for applications that require very high throughput rates or that involve materials with very high temperatures or corrosive properties.
Design Principles

Screw Geometry
The screw geometry is a critical factor in the design of screw conveyors. The most common screw geometries are the helix and the ribbon. The helix geometry is suitable for conveying free-flowing materials, while the ribbon geometry is better suited for handling cohesive or sticky materials. The pitch, diameter, and length of the screw are also important factors to consider when designing a screw conveyor. The pitch determines the amount of material that is conveyed per revolution, while the diameter and length of the screw determine the capacity of the conveyor.
Material Specifications
The material specifications of the screw are crucial to the performance and durability of the conveyor. The most common materials used for screw conveyors are carbon steel, stainless steel, and abrasion-resistant alloys. The selection of the material depends on the type of material being conveyed, the operating conditions, and the required durability. The thickness of the screw also plays a role in the durability of the conveyor.
Drive Mechanisms
The drive mechanism is responsible for transmitting power to the screw and moving the material along the conveyor. The most common drive mechanisms are belt drives, direct drives, and chain drives. Belt drives are commonly used for low power applications, while direct drives are used for high power applications. Chain drives are used for applications that require high torque and heavy loads. The selection of the drive mechanism depends on the power requirements, the operating conditions, and the required speed and torque.
In summary, the design of screw conveyors involves careful consideration of the screw geometry, material specifications, and drive mechanisms. By selecting the appropriate design parameters, screw conveyors can be optimized for performance, durability, and efficiency.
Types of Screw Conveyors

Screw conveyors are used for transferring bulk materials from one point to another. These conveyors are available in different types depending on the application and the material being conveyed. The following are the most common types of screw conveyors.
Horizontal Screw Conveyors
Horizontal screw conveyors are used for transferring materials horizontally. They are typically used for short to medium distance applications. These conveyors are designed to move materials at a constant rate and are available in different sizes, capacities, and materials of construction.
Inclined Screw Conveyors
Inclined screw conveyors are used for transferring materials at an angle. They are typically used for medium to long distance applications. These conveyors are designed to move materials at a constant rate and are available in different sizes, capacities, and materials of construction.
Vertical Screw Conveyors
Vertical screw conveyors are used for transferring materials vertically. They are typically used for short to medium distance applications. These conveyors are designed to move materials at a constant rate and are available in different sizes, capacities, and materials of construction.
Shaftless Screw Conveyors
Shaftless screw conveyors are used for transferring materials that are sticky or difficult to convey with a traditional shafted screw conveyor. They are typically used for short to medium distance applications. These conveyors are designed to move materials at a constant rate and are available in different sizes, capacities, and materials of construction.
In conclusion, screw conveyors are versatile and efficient machines that are used in a variety of industries for bulk material handling. The type of screw conveyor used depends on the application and the material being conveyed.
Operational Considerations

Throughput Capacity
The throughput capacity of screw conveyors is an essential factor to consider when selecting the appropriate screw conveyor for an application. The throughput capacity is the amount of material that can be conveyed per unit of time. It is determined by the screw conveyor’s diameter, pitch, and speed.
A larger diameter screw conveyor with a higher pitch and speed will have a higher throughput capacity. However, it is important to note that increasing the speed of the screw conveyor can lead to increased wear and tear on the equipment, which can result in higher maintenance costs.
Feeding and Discharge Points
Another important operational consideration for screw conveyors is the feeding and discharge points. The feeding point should be designed to ensure a consistent and uniform flow of material into the conveyor. If the material is not fed evenly, it can lead to blockages and other issues.
Similarly, the discharge point should be designed to ensure a smooth and consistent flow of material out of the conveyor. If the discharge point is not designed properly, it can lead to material buildup and blockages, which can cause damage to the conveyor.
To ensure optimal performance, it is recommended to consult with a screw conveyor manufacturer to determine the appropriate feeding and discharge points for a specific application.
Overall, considering these operational factors can help ensure the efficient and reliable operation of screw conveyors in various industrial applications.
Maintenance and Safety
Routine Inspection
Regular inspection of screw conveyors is essential to ensure that they operate efficiently and safely. The inspection should include checking for any signs of wear or damage to the conveyor components, such as the flighting, bearings, and seals. The conveyor should also be checked for any signs of misalignment or excessive vibration. If any issues are found during the inspection, they should be addressed immediately to prevent further damage or safety hazards.
Lubrication Requirements
Proper lubrication is crucial to the performance and longevity of screw conveyors. The lubrication requirements will depend on the specific conveyor design and application. It is important to follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for lubrication intervals and types of lubricants to use. Over-lubrication can lead to excess buildup and blockages, while under-lubrication can cause premature wear and damage to the conveyor components.
Safety Guards and Procedures
Safety guards and procedures are critical to protecting workers from potential hazards associated with screw conveyors. Guards should be installed to prevent access to moving parts, such as the rotating flighting and drive shaft. Workers should also be trained on proper lockout/tagout procedures to ensure that the conveyor is de-energized and locked out before any maintenance or repairs are performed. Additionally, workers should be trained on proper lifting techniques to prevent injuries when handling heavy conveyor components.
Overall, proper maintenance and safety procedures are essential to the safe and efficient operation of screw conveyors. Regular inspections, proper lubrication, and the use of safety guards and procedures can help prevent accidents and prolong the life of the conveyor.
Installation Guidelines
Proper installation of screw conveyors is essential for their efficient operation and longevity. Here are some guidelines to follow during installation:
1. Preparation
Before installing the screw conveyor, ensure that the installation site is clean and free from debris. Check that the conveyor components are in good condition and that all necessary tools and equipment are available. It is also important to have a clear understanding of the installation process and any safety precautions that need to be taken.
2. Alignment
Proper alignment of the screw conveyor is crucial for its smooth operation. The conveyor should be aligned both horizontally and vertically to ensure that it is level and straight. Misalignment can cause excessive wear and tear on the conveyor components and lead to premature failure.
3. Mounting
Mount the conveyor securely to a stable foundation using appropriate fasteners. The mounting surface should be level and capable of supporting the weight of the conveyor and the material being conveyed. It is important to follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for mounting and to ensure that the conveyor is properly supported.
4. Electrical Connections
If the screw conveyor is electrically powered, ensure that all electrical connections are made according to the manufacturer’s specifications. Use appropriate wiring and connectors, and follow all safety guidelines for electrical installations.
5. Testing
After installation, test the conveyor to ensure that it is operating properly. Check for any unusual noises, vibrations, or other signs of malfunction. Make any necessary adjustments or repairs before putting the conveyor into service.
By following these installation guidelines, the screw conveyor can be installed safely and efficiently, ensuring reliable operation for years to come.
Troubleshooting and Problem Solving
Screw conveyors are generally reliable and require minimal maintenance. However, problems can occur from time to time. Here are some common issues that may arise and how to troubleshoot them:
Material Buildup
Material buildup can occur when the screw conveyor is not properly designed or when the material being conveyed is sticky or has a tendency to clump together. This can cause the screw to become clogged, leading to a decrease in throughput or even a complete stoppage.
To prevent material buildup, it is important to ensure that the screw conveyor is properly designed for the specific material being conveyed. Additionally, adding a spray system to the conveyor can help to keep the material moving smoothly.
Excessive Noise
Excessive noise can be caused by a variety of factors, including worn bearings, misaligned components, or loose bolts. If left unchecked, excessive noise can lead to further damage and decreased efficiency.
To troubleshoot excessive noise, start by checking the bearings and replacing any that are worn. Next, check for misaligned components and tighten any loose bolts. Finally, consider adding sound insulation to the conveyor to reduce noise levels.
Overheating
Overheating can occur when the conveyor is overloaded or when the material being conveyed is too hot. This can cause damage to the conveyor components and decrease efficiency.
To prevent overheating, make sure that the conveyor is not overloaded and that the material being conveyed is within the recommended temperature range. Additionally, adding cooling fans to the conveyor can help to dissipate heat and prevent overheating.
By addressing these common issues, screw conveyor operators can ensure that their equipment runs smoothly and efficiently, minimizing downtime and maximizing productivity.
Applications and Industries
Screw conveyors are used in a wide range of applications and industries due to their versatility and efficiency. Some of the most common applications include:
Agriculture
Screw conveyors are used in agriculture for handling and transporting grains, seeds, and other agricultural products. They can be used for loading and unloading trucks, filling and emptying silos, and conveying materials between processing equipment.
Food Processing
In the food processing industry, screw conveyors are used for transporting and handling various food products such as flour, sugar, spices, and grains. They are also used for conveying food waste and byproducts to disposal areas.
Mining
Screw conveyors are commonly used in the mining industry for transporting and handling bulk materials such as coal, ores, and minerals. They are used for loading and unloading trucks and railcars, as well as conveying materials between processing equipment.
Waste Management
Screw conveyors are used in waste management for transporting and handling various types of waste such as sewage sludge, industrial waste, and municipal solid waste. They are also used for conveying recyclable materials to processing facilities.
Overall, screw conveyors are a reliable and cost-effective solution for handling and transporting bulk materials in a wide range of industries and applications.
Advancements and Innovations
Over the years, screw conveyors have undergone significant advancements and innovations that have made them more efficient and reliable. Some of these advancements and innovations include:
1. Improved Materials
Screw conveyors are now made from high-quality materials that are resistant to wear and tear. Stainless steel, for instance, is a popular material used in the construction of screw conveyors due to its durability and corrosion-resistant properties. Other materials used include carbon steel and plastic.
2. Advanced Design
The design of screw conveyors has evolved over the years to improve their performance. The use of computer-aided design (CAD) software has made it possible to create more complex and efficient screw conveyor designs. Additionally, the incorporation of advanced features such as variable frequency drives (VFDs) has made it possible to control the speed and torque of screw conveyors, resulting in better performance and energy efficiency.
3. Automation
Automation has become an integral part of screw conveyor systems, making them more efficient and reliable. Automated screw conveyors can be programmed to operate at specific times, speeds, and temperatures, reducing the need for manual intervention. This has not only improved the efficiency of screw conveyors but also reduced the risk of accidents and injuries.
In conclusion, advancements and innovations in screw conveyor technology have made them more efficient, reliable, and safer to use. These improvements have also made it possible to customize screw conveyor systems to meet specific needs and requirements.
Regulatory Standards and Compliance
Screw conveyors are subject to various regulatory standards and compliance requirements to ensure their safe and efficient operation. These regulations are designed to protect workers and the environment from potential hazards associated with the use of screw conveyors.
One of the most important regulatory standards for screw conveyors is the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) regulations. OSHA sets standards for the safe use of machinery and equipment, including screw conveyors. These standards cover a range of topics, such as guarding, lockout/tagout, and hazard communication.
In addition to OSHA regulations, screw conveyors may also be subject to other regulatory standards and compliance requirements, such as those set by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) or state and local agencies. These regulations may cover issues such as air emissions, noise levels, and waste disposal.
To ensure compliance with these regulations, it is important to work with a reputable screw conveyor manufacturer that understands the regulatory landscape and can provide equipment that meets all applicable standards. Additionally, regular maintenance and inspections can help ensure continued compliance and safe operation of screw conveyors.
Overall, compliance with regulatory standards is essential for the safe and efficient operation of screw conveyors. By working with knowledgeable manufacturers and following all applicable regulations, users can ensure that their screw conveyors are operating safely and effectively.
Selection and Sizing Criteria
When selecting a screw conveyor, it is important to consider the specific application requirements. Factors such as material type, bulk density, flow rate, and conveyor length should be taken into account to ensure optimal performance.
The first step in selecting a screw conveyor is to determine the required capacity. This can be calculated using the material’s bulk density and desired flow rate. Once the capacity is determined, the conveyor’s diameter and pitch can be selected based on the required throughput.
Another important factor to consider is the material’s characteristics. Abrasive or corrosive materials may require special materials for the conveyor’s construction. Additionally, materials with poor flowability may require a larger diameter or steeper pitch to prevent clogging.
The conveyor’s length should also be considered when selecting a screw conveyor. Longer conveyors may require additional support to prevent sagging or excessive deflection. It is recommended to consult with a manufacturer or engineer to ensure proper conveyor design.
In summary, selecting and sizing a screw conveyor requires careful consideration of the application’s specific requirements. Material characteristics, flow rate, capacity, and conveyor length should all be taken into account to ensure optimal conveyor performance.



